Bed Sore Care

Bed sore is known by medical community as Pressure Injury. It is happening mostly to those who are immobile - bed bound and wheel chair bound patients. Prolonged non-movement will have pressure build against boney part of the body, coupled with friction on the skin. Area affected will experience reduce blood flow, tissue injury, skin tear, following with wound appearing. High risk affected areas are tailbone, heels, hips, back, elbows, and the back of the head when lying down for a long period of time. It is the area of sacrum or trochanter for those on long term wheelchair that will develop risk.
High risk area prone to Pressure Injury


Pressure injury early stage (stage 1 & 2) developed discolored vulnerable skin with mild to moderate tissue damage on the skin surface. Treated properly and easing off the continuous pressure, it would heal in days or a few weeks.
Pressure Injury (Bed Sore) stages
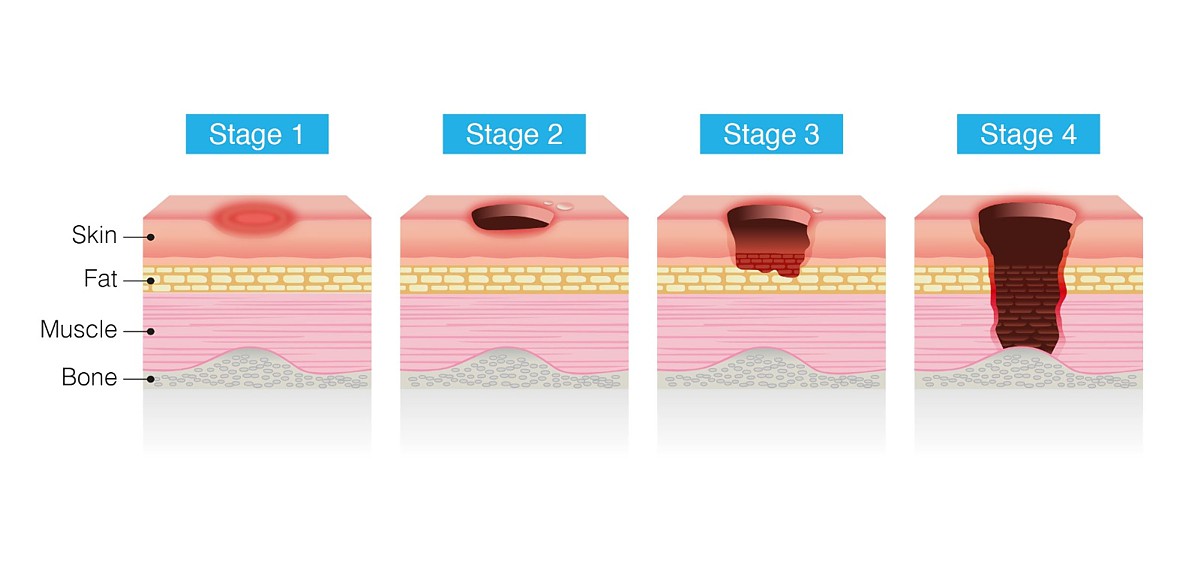
When the Pressure Injury deteriorate to later stage, a deeper wound will develop (stage 3 or 4) exposing deep tissue or bone. This will take a longer multiple months to heal even with deployment of surgical management and advance wound care treatment.
Key strategy to circumvent Pressure Injury is to intervene early, deflect pressure build-up on affected area & treat the affected skin deterioration as early as possible by an experienced healthcare professional. Changing the static position of the patient constantly, Pic 4 applying vulnerable skin protection lotion to encourage skin healing would reverse early stage PI condition.
Late stage Pressure Injury with a deeper open wound are exposed chances of wound infection and might lead to development of high risk sepsis. Consult a medical professional for medical care, surgical intervention and continuous cleansing with effective antimicrobial dressing to avoid deterioration of the wound bed and encourage proper healing.
Changing static position of patient

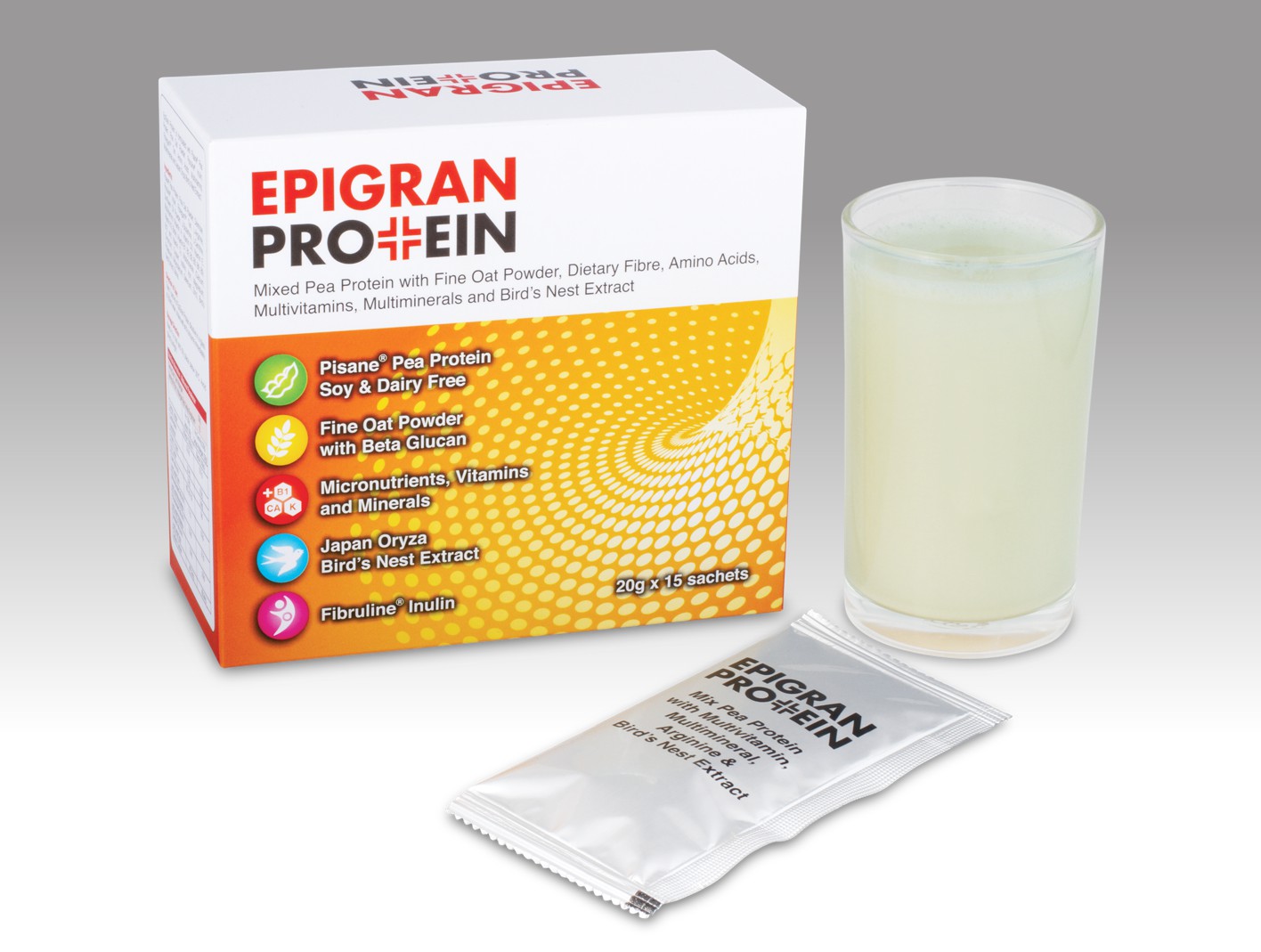

 Nourish to flourish - Nutrition matters in healing
Nourish to flourish - Nutrition matters in healing
- Pressure Injury wound healing involves multiple aspect of healthcare practice. Medical professional will monitor control of underlying disease. Constant nursing care is recommended when there is Pressure Injury. They would have to carry out wound care procedure on injury and nutritional advocate is an essential building block to ensure wound recovery.
- Pressure injury clinical practice guideline has highlight the importance of nutrition in cases of recovery. Wound healing Granulation and Epithelialization need a lot of energy, protein especially those patient with pressure injury. Due to the nature of their immobility, most of these patient are unable to have enough calories intake, absorbing the right nutrients and sufficient hydration.
- Nourishing the patient with introduction of fortified food is recommended by the guideline for patient that could not intake sufficient calories and protein in a normal dietary intake . Fortified high calorie, high protein nutritional supplement in between meals can support strong skin and muscle to aid healing and prevent pressure injury.

Caregiver note to take care of pressure injury patient
- Ensure good incontinence care, keep skin clean and dry.
- Examine frequently all high risk skin area to avoid constant pressure, apply cushion & lotion for early compromised area.
- High risk skin area should be examined everyday to discover pressure point.
- If patient is bed bound, ensure turning & movement, shifting weight every 2 hours.
- Soft cushioned surfaced items could be used to relief pressure.
- Ensure patient receive adequate nutrition & hydration, high protein healthy food with sufficient liquid intake.
- Prevention is key to avoid Pressure Injury, if discovered pressure injury, please seek help from medical professionals as soon as possible.
- Consider using ripple mattresses or alternating-pressure mattresses that may redistribute pressure and promoting better circulation and ease off continuous pressure build-up at the same idle position.
NPUAP/EPUAP/PPPIA Nutrition Guidelines 2014 states
Provides energy of 30-35 kcal/kg body weight for adults with Pressure Injury OR at risk of pressure injury.Offer fortified foods and/or high-calorie, high-protein oral nutritional supplements between meals if nutritional requirements CANNOT be achieved by dietary intake.

Professional wound care, skin care, nutritional products available @ major pharmacies






